Grant for Mobile WiFi Access Points
Dr. Nelakuditi and his ARENA research lab have received an NSF grant award for their project on "Infrastructure Mobility". This research is exploring how to build and program mobile WiFi access points, on wheels, that change position to improve signal reception. Imagine a small robot that moves within the false ceiling of a large building to provide better signal to its users.
Abstract
Mobile computing has traditionally implied mobile clients connected to a static infrastructure. This project breaks away from this point of view and envisions the possibility of injecting mobility into infrastructure. The PIs envision a WiFi access point on wheels that moves to optimize desired performance metrics. Movements need not necessarily be all around the floor of a home or office, neither do they have to operate on batteries, or connect wirelessly to the Internet. At homes, they could remain tethered to power and Ethernet outlets while moving in small areas (perhaps under the study table). In offices of the future, perhaps APs could move on tracks installed on top of false ceilings. The cloud could perhaps coordinate their mobility based on how users move within the environment, or how traffic and interferences change in the network. This project explores the viability of this vision and will present thorough measurements from various home/office environments. Initial measurements with moving WiFi APs in residential and enterprise environments exhibit promise. Analysis finds that complex multipath characteristics of indoor environments cause large fluctuations in link quality even when the antenna moves in the scale of one foot. Mobile APs can leverage this spatial variation by relocating to a pixel that is strong for its own clients and yet weak from its interferers. When multiple APs are coordinated by a central controller, the motion paths of the APs need to be jointly planned to optimize global network parameters. Heuristics will be developed that first assume the knowledge of AP locations; based on the outcome of this heuristic, the assumption might be relaxed. The project will also consider client mobility and how APs adapt to them, perhaps based on the quality of channel changes available from channel state information (CSI) in today's WiFi cards. If mobility proves to offer additional gains despite the advances in current technologies, robotic wireless networking might become an important and exciting direction of the future.
 PhD student
PhD student 
 Our
Our  We would like to welcome our newest assistant professor,
We would like to welcome our newest assistant professor,  We would like to congratulate our very own
We would like to congratulate our very own 
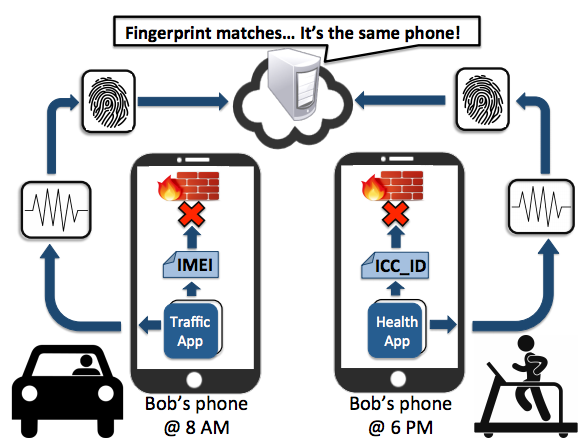
 We would like to congratulate
We would like to congratulate 
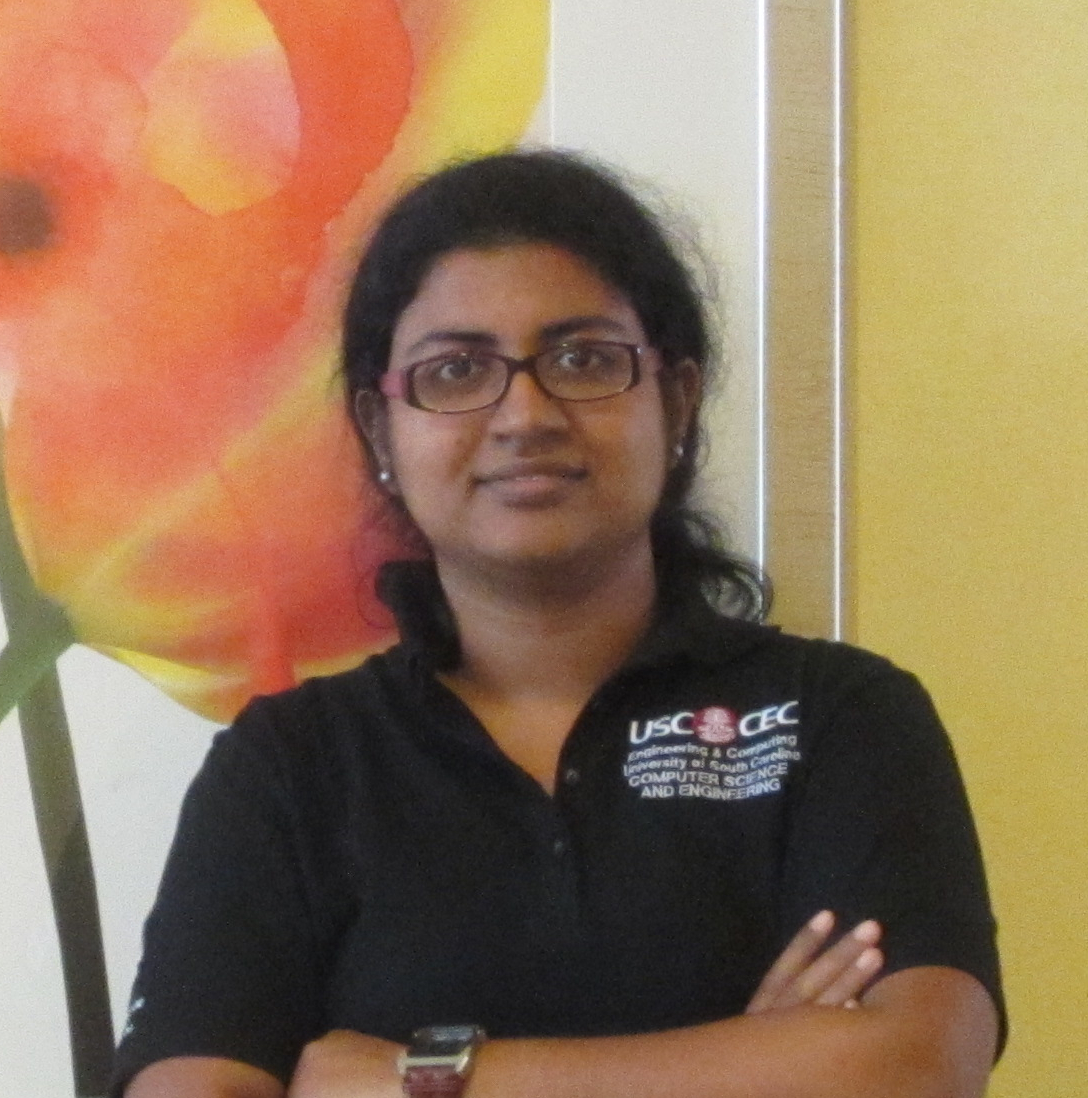 Two of our graduate students,
Two of our graduate students,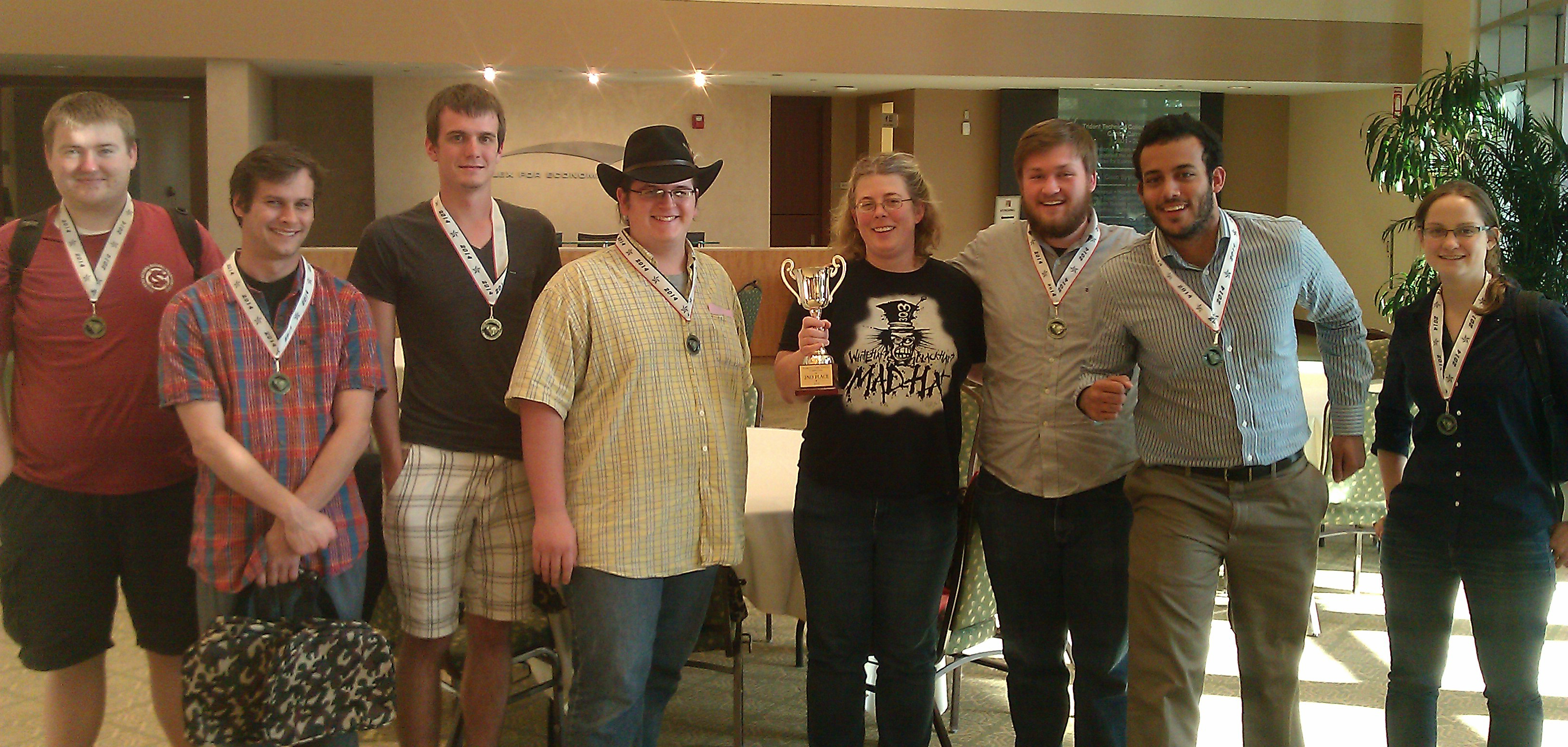 


 We congratulate the following graduate students for receiving recognition for their outstanding work.
We congratulate the following graduate students for receiving recognition for their outstanding work.